How to Create Email Accounts on Shared Hosting
Read the guide below to learn how to manage email accounts on your shared hosting.

UK hosting providers will gladly share their knowledge, expertise, and insights about shared hosting. Here’s a comprehensive and clear explanation for setting up an email account along with other essential features which include email forwarding.
Creating an Email Address
Create your email address after acquiring a hosting account and adding your domain to the control panel.
- Log in to your control panel.

- Click the Email icon after gaining access to that panel.
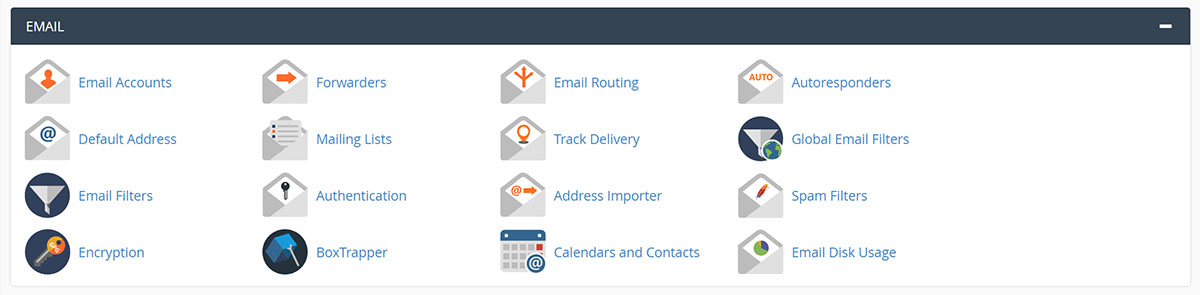
- Create the email address at Mail Manager. Set up a pseudonym or alias which refers to the Mail Forward.
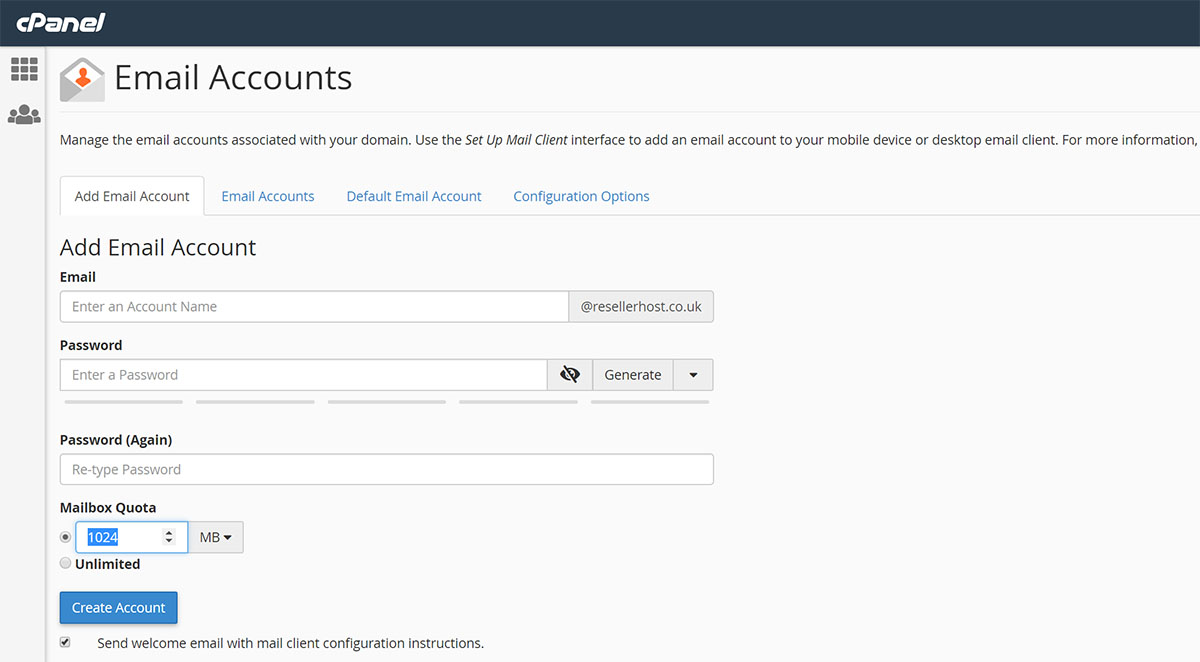
- Select the “Add Email Account” tab.

- Think of a name for the Email Box. See to it that you place a check mark beside the Mailbox.
- Make sure you have a strong password for the Email Box.
- Scroll to the bottom of the web page after creating your email account. Click Create Account.
Mail Client’s General Settings
You will use specific information and settings for the configuration of email addresses in the Mail Client.
- Username
- Email Address
- Type of Account (Internet Message Access Protocol/IMAP or Post Office Protocol 3/POP3)
- Incoming and Outgoing Server Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) – yourdomain.com for both
- Username and Password/ Complete Email Address and Password
Proceed to Advanced or More Settings in the email client to verify the port settings after suppling the appropriate information. Incoming Server Port (POP3) is 110 while IMAP is 143. Hosts normally recommend the Port Setting of 25 or 587 for the outgoing server’s SMTP. After verifying the port setting, see to it the server calls for an encrypted connection or Security Sockets Layer (SSL). Accomplishing all these steps means you have successfully configured your email account.
Email Access in your Browser
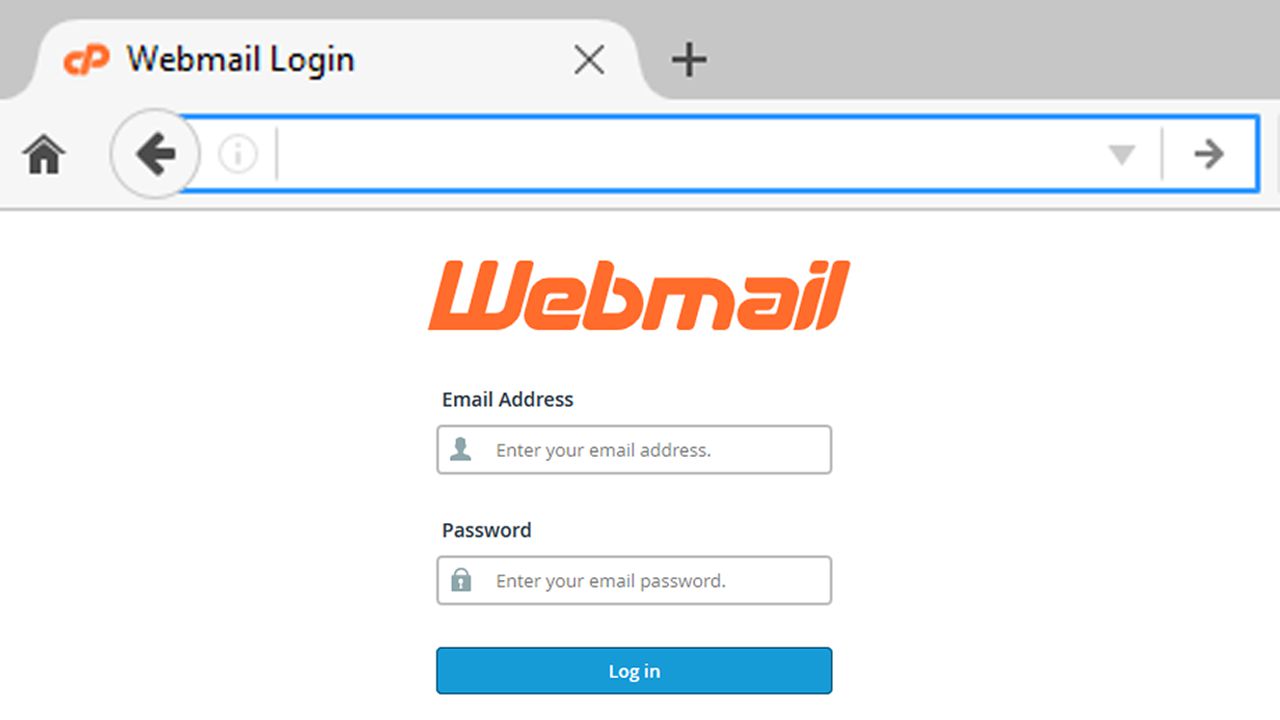
There is another way of accessing the web browser rather than logging in to your hosting account.
- Type yourdomain.com in the address bar.
- Enter your username which should be your complete email address and password.
- You may now send and receive email messages after completing successful login.
Valuable Features
There are vital features that users must become familiar with in the shared hosting process.
Email Forwarding refers to resending messages from your email address to other addresses. You can set up email forwarding for free. One notable feature allows users to create personalized addresses for domains as well as forward messages to selected recipients.
The service is usually available for domains pointing to Basic and Back-up Domain Name Systems (DNS) as well as Premium and Free DNS systems. You can possibly initiate around 100 forwarding addresses on these nameservers and maximum of 50 on Backup systems.
Here are the steps in setting up Email Forwarding for your domain names:
- Sign into your hosting account.
- Choose the Domain List from the left sidebar along the main display area of the interface.
- Go to the Advanced DNS key on top of the page.
- Look for Mail Settings Choose Email Forwarding from your drop-down menu. By saving all changes, you automatically set up the Mail Exchanger Record, a certified and confirmed resource record in the DNS specifying mail servers responsible for receiving messages for the recipient’s domain.
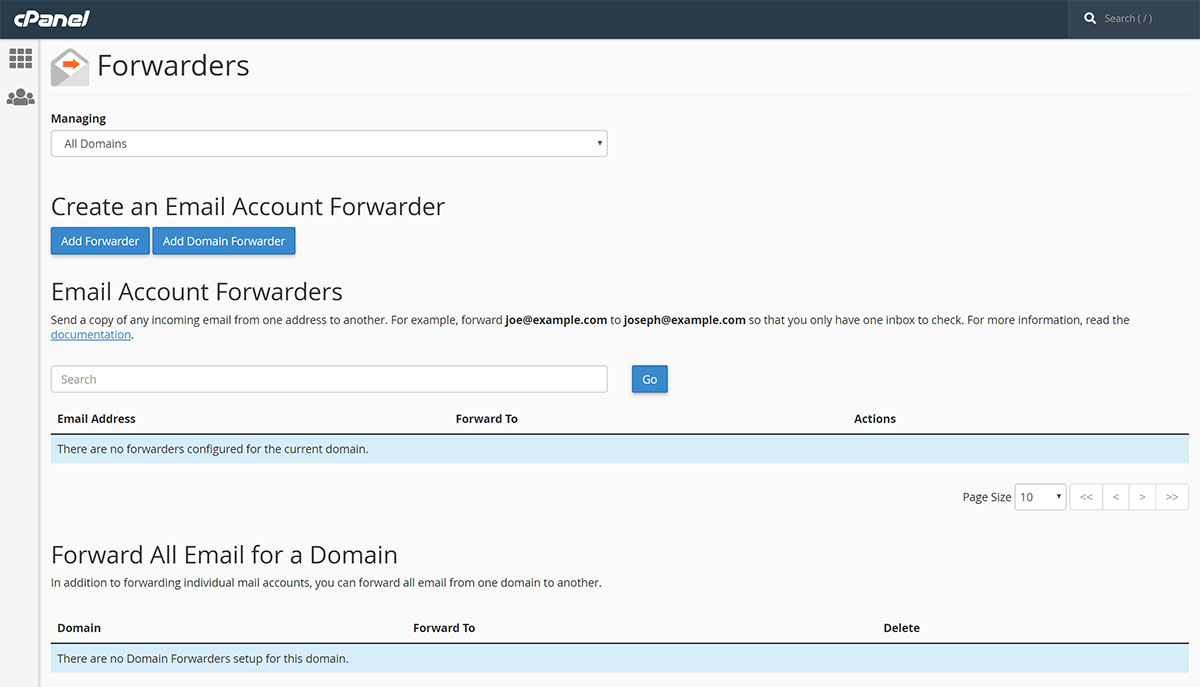
- Select the domain tab at the top of the page. Scroll down to Redirect Email
- Click Add Forwarder
- Accomplish the Alias as well as Forward to fields with the necessary information. Click the checkmark icon to save your changes.
- Alias will be the name of your forwarding mailbox. See to it the Forward to field contains the complete destination email address.
Allocate at least one hour for the complete setup of new mailboxes on your forwarding mail server. Test the mail service after activation of your settings.
The delivery of test mails from one address set as Forwarded to will most likely be unsuccessful. Use a different email address for testing the forwarding service.
Emails with zip attachment get blocked automatically by the Free Forwarding spam filter. This kind of emails will not be transmitted to the email addresses set as Forwarded to.
Compatibility with Clients and Devices

Users who started generating email messages for their service or enterprise will likely test them several times. The purpose is to find out if the spelling of words, graphics, and overall appearance are correct. Do not forget to check how these function for a variety of email clients.
For instance, the text may look good on big monitors. However, it may not scale down properly to the smaller screens of mobile devices like phones and tablets. In the same way, the monthly marketing mailer looks okay in Gmail but does not fit with Microsoft Outlook. These situations make testing critical. Test your emails on clients as well as devices to determine the following:
- Messages are not too lengthy in small screens.
- Images show correctly in different clients.
- Templates and custom codes match multiple clients or browsers clients use to view your email messages.
If possible, choose a platform with the feature allowing you to preview your message in over 40 different browsers and clients. Through this approach, you do not have to worry regarding messages that fit one system but does not work in another.
Options for Highest Accessibility

You cannot avoid some customers failing to see your images or use the standard client to read your email messages. The reason is people from all over the globe access the worldwide web and its features differently. Therefore, you need plain text as well as viewing online alternatives for maximum access.
There are several options in making your email messages more accessible. However, always make sure to include the plain text version. You can easily decipher plain text not including images and codes on any screen or device. Use technology such as the screen reader software.
Almost all email tools automatically produce the plain text version of any Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)-based messages. However, you may want to check out these messages to confirm easy reading as well as applicable line breaks and other essential attributes.
Another distinct feature normally added by design and should not be missed is the option to view messages in a browser. The link enables users to see your messages if images fail to load or the email client does not work regardless of the testing. The View Online link must be prominent with the topmost right or left corner as the most ideal place. Fewer browsers will complain if they fail to read messages or discern images that you put together.
Backup and Protection

Even the most reliable hardware fails at the most unexpected moment. Once this happens, the results can be disastrous. A backup system means your email system gets up and running right away. Any emails lost due to the failure may be recovered from the sending site. With the appropriate backup, messages stored in the local drive can be recovered fast enough except for those in the server.
Protection is designed for viruses, spyware, and spam. Remember that your systems are vulnerable to breaches by bugs, worm (anomalous computer programs), and malicious ware or malware. The email is the biggest portal where these attacks usually take place. Regular virus as well as spyware scanning prevents suspicious attachments from getting through.
Email addresses are also prone to spam. These emails are like paper junk that you receive in your physical mailboxes. Spam mails fill up an inbox of users quickly. Effective spam filters can help repel spam mails. Otherwise, you must install a separate network device to keep away the junk before it penetrates your system.
Push Email
Majority of email systems without the push mail requires users in refreshing their inbox before new mails are received from senders. With the push mail system in place, new emails are transmitted to the inbox which eliminates the need for refreshing. This is most applicable for mobile devices like smartphones.
Active syncing is an equally important feature. Emails come into the server and forwarded to the user or read through the IMAP on desktops, laptops, or tablets. With the sync capacity, emails are sent to mobile phones easily.
Remember that emails remain as one of the business owner’s critical lifelines. You must keep it up and running round the clock. Protect your system from unexpected crashes, spam, and hackers who try to infiltrate from time to time. Achieving these targets will ensure client satisfaction and your business bottom line. Look for a shared hosting company that will meet all your requirements.
Looking what to read next? Visit Guide to Setting Up an Email Forwarder in cPanel & Webmail.
